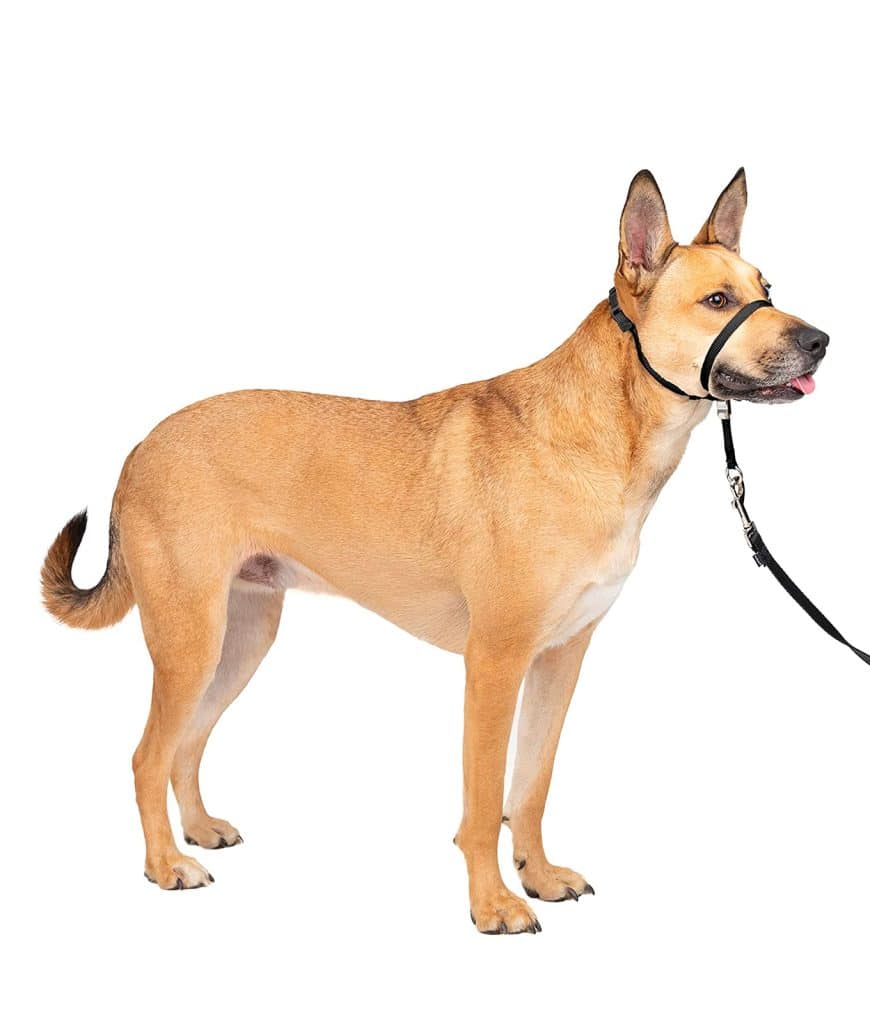
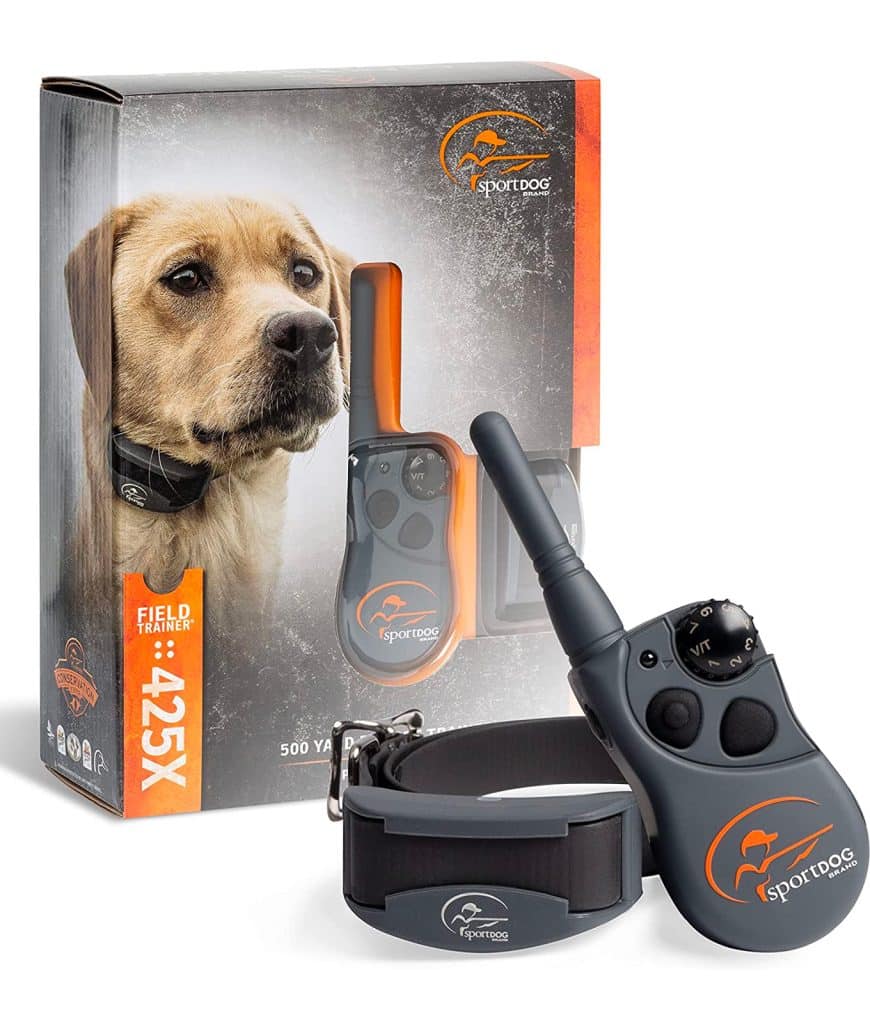
When it comes to dog training, choosing the suitable collar is essential, as it can significantly impact the effectiveness of your training sessions.
Various types of collars are available, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. From traditional buckle collars to martingale collars and even remote training collars, the options can be overwhelming.
In this article, we will explore the different types of collars to help you make an informed decision based on your dog’s needs and training goals.
Whether you have a stubborn pup or a quick learner, finding the perfect collar can make all the difference in achieving successful training outcomes.
1. Importance of Choosing the Right Collar
When it comes to dog training, choosing a suitable collar is paramount. It ensures the safety and comfort of your furry friend and plays a vital role in practical training. Your collar should be tailored to address specific training goals while considering your dog’s needs and characteristics.
1.1 Ensuring Safety and Comfort
One of the primary reasons for selecting the right collar is to ensure the safety and comfort of your dog. A well-fitted collar prevents your dog from slipping out and getting lost during walks or outdoor activities. It should be comfortable enough to wear for extended periods without causing any discomfort or irritation.
1.2 Effective Training Tool
A properly chosen collar can be an invaluable tool in dog training. It allows you to have better control over your dog’s movements, making it easier to teach commands, correct unwanted behaviors, and reinforce positive behaviors. The right collar can aid in achieving desired training outcomes more efficiently and quickly.
1.3 Addressing Specific Training Goals
Different types of collars are designed to address different training goals. Depending on your specific training objectives, you may need a collar that helps with loose leash walking, discourages pulling, or provides gentle control for dogs with aggression issues. Choosing a suitable collar can significantly contribute to achieving your training goals effectively.
2. Different Types of Collars
Understanding the various types of collars available can help you make an informed decision based on your dog’s needs and the training goals you want to achieve. Let’s explore some of the most common types of collars and their purposes.
2.1 Flat Collars
Flat collars are the most basic and commonly used type of collar. They consist of a simple strap with a buckle or snap closure. Flat collars are suitable for everyday use, identification purposes, and leash attachment. They come in various materials and designs, allowing you to choose according to your dog’s size, comfort, and style preferences.
2.2 Martingale Collars
Martingale collars, also known as limited-slip collars, are designed to provide more control without choking or causing discomfort to your dog. These collars have a loop that can tighten when the dog pulls on the leash, preventing them from slipping out. Martingale collars are particularly useful for dogs that have a tendency to escape from traditional flat collars.
2.3 Head Collars
Head collars, such as the Gentle Leader or Halti, are designed to provide control by gently guiding your dog’s head and redirecting its attention. These collars fit around the dog’s muzzle and neck, giving you control over their movements and reducing pulling behavior. Head collars are effective for dogs prone to pulling or those in need of additional control during walks.
2.4 Prong Collars
Prong collars, also known as pinch collars, consist of a series of metal links with prongs that apply pressure when the dog pulls. This collar is primarily used for dogs with persistent pulling or behavioral issues. However, it is essential to note that prong collars should only be used under the guidance of a professional trainer, as they can cause discomfort if used incorrectly.
2.5 Slip Collars
Slip collars, commonly known as choke collars, are designed to tighten around the dog’s neck when pressure is applied. These collars are typically made of chain or nylon, and their tightness can be adjusted. Slip collars are commonly used for training dogs in obedience and are effective when used correctly and with proper training techniques.
2.6 Harnesses
Harnesses are collar alternatives that wrap around the dog’s chest and torso. They distribute pressure more evenly across the body, reducing strain on the neck and throat. Harnesses are ideal for dogs with respiratory issues, those prone to pulling, or those needing additional support. There are various types of harnesses available, including front-clip, back-clip, and no-pull harnesses.
3. Factors to Consider
Several factors should be considered when choosing the right collar for your dog. These factors help determine which collar type will best suit your dog’s needs and training goals.
3.1 Breed and Size
The breed and size of your dog play a crucial role in collar selection. Smaller dogs may require lightweight and adjustable collars, while larger dogs may need wider and more durable options. Breeds with short muzzles or delicate necks may benefit from harnesses rather than traditional collars.
3.2 Temperament and Behavior
Understanding your dog’s temperament and behavior is essential in determining the appropriate collar. For example, if your dog tends to pull during walks, a head collar or harness may be more effective in providing control. If your dog is easily startled or anxious, a Gentle Leader or martingale collar may help in reducing their stress levels.
3.3 Training Objectives
Your training objectives also influence the collar choice. A gentle or front-clip harness may be the best option if you are focused on loose-leash walking. For obedience training, slip and martingale collars provide more control over your dog’s movements. Understanding your specific training goals will guide you in selecting the most suitable collar.
3.4 Physical Limitations
Consider any physical limitations or health conditions your dog may have. Dogs with respiratory issues or neck injuries may require harnesses that alleviate pressure on their necks. Seek advice from your veterinarian if your dog has any physical limitations that require a specialized collar.
4. Flat Collars
4.1 Basic Design and Function
Flat collars are characterized by their simple design, consisting of a buckle or snap closure attached to a strap. They are typically made of nylon, leather, or fabric materials. Flat collars can be easily adjusted to ensure a proper fit around your dog’s neck.
4.2 Best Suited for
Flat collars are best suited for dogs that are already well-trained and under control during walks. They are effective for attaching identification tags and leashes, making them suitable for everyday use and outings.
4.3 Pros and Cons
One of the biggest advantages of flat collars is their simplicity and ease of use. They are affordable and widely available in various colors and designs to suit your style preferences. However, flat collars may not be suitable for dogs that pull excessively or have aggression issues, as they provide limited control.
4.4 Proper Usage Tips
When using a flat collar, ensure that it is adjusted to fit snugly but not too tightly around your dog’s neck. It should allow you to insert two fingers comfortably between the collar and your dog’s neck. Regularly check the collar for any signs of wear or damage and replace it if necessary.
5. Martingale Collars
5.1 Basic Design and Function
Martingale collars consist of a wide loop that fits loosely around the dog’s neck and a smaller loop that tightens when tension is applied. This tightening action prevents the dog from slipping out of the collar while still providing a comfortable fit when there is no tension.
5.2 Best Suited for
Martingale collars are best suited for dogs that tend to back out of traditional flat collars or have narrow heads. They are particularly effective for breeds like Greyhounds, Whippets, and Afghan Hounds, which have slim necks and larger heads.
5.3 Pros and Cons
One of the main advantages of martingale collars is their ability to provide control without tightening too much or causing discomfort. They offer a secure fit and prevent dogs from escaping during walks. However, it is important to ensure proper adjustment and use a backup leash attachment if the smaller loop fails.
5.4 Proper Usage Tips
To properly use a martingale collar, adjust the larger loop to fit around your dog’s neck and the smaller loop to allow for a comfortable fit when there is no tension. The collar should tighten only to a limited degree when the dog pulls. Always use a relevant leash attachment and the martingale collar for added security.
6. Head Collars
6.1 Basic Design and Function
Head collars like the Gentle Leader or Halti are designed to fit over your dog’s muzzle and around the back of their neck. They utilize steering your dog’s head to control its movements. Head collars typically have an additional strap that attaches to your dog’s regular collar for added security.
6.2 Best Suited for
Head collars are best suited for dogs that tend to pull excessively during walks or require additional control. They can be particularly effective for large or strong dogs that may be difficult to manage using traditional collars.
6.3 Pros and Cons
One of the advantages of head collars is the control they provide by steering the dog’s head and reducing pulling behaviors. They are generally well-tolerated by dogs when introduced properly and used correctly. However, some dogs may initially resist wearing a head collar or exhibit resistance to the steering action.
6.4 Proper Usage Tips
When using a head collar, ensure it is properly secured and adjusted around your dog’s muzzle and neck. Introduce it gradually and associate positive experiences with wearing the collar. Avoid excessive jerking or pulling on the leash, which can cause discomfort and harm your dog’s neck or head.
7. Prong Collars
7.1 Basic Design and Function
Prong collars, or pinch collars, consist of interlocking metal links with prongs that press against the dog’s neck when tension is applied. The prongs provide a mild corrective sensation, mimicking the pressure a mother dog would use to correct her puppies.
7.2 Best Suited for
Prong collars are generally recommended for dogs that have persistent pulling behavior or exhibit signs of aggression. They are best suited for large or powerful dogs that may be difficult to control using other types of collars.
7.3 Pros and Cons
One of the advantages of prong collars is their potential effectiveness in reducing pulling or aggression when used correctly and under professional guidance. They can provide instant feedback to the dog, facilitating faster learning. However, prong collars require careful handling and should only be used under the guidance of a professional trainer to prevent misuse or potential harm.
7.4 Proper Usage Tips
If you choose to use a prong collar, consult a professional trainer who can guide you on proper fitting and usage techniques. Prong collars should be used with caution and never for prolonged periods. Avoid jerking or yanking the leash, as this can cause discomfort or injury to your dog.
8. Slip Collars
8.1 Basic Design and Function
Slip collars, also known as choke collars, consist of a chain or nylon loop that tightens around the dog’s neck when pressure is applied. This tightening action functions as a correction to discourage unwanted behaviors.
8.2 Best Suited for
Slip collars are best suited for dogs already trained to respond to leash pressure and require occasional reminders. They are commonly used in obedience training, particularly for dogs participating in trials or competitions.
8.3 Pros and Cons
One advantage of slip collars is their simplicity and ease of use. They provide quick correction when necessary and can effectively reinforce training commands. However, slip collars should only be used when appropriate and under the guidance of a knowledgeable trainer, as improper usage can cause injury or discomfort.
8.4 Proper Usage Tips
When using a slip collar, it is crucial to ensure it is properly fitted and adjusted. The collar should be loose when there is no tension on the leash but tighten to a limited degree when the dog pulls. Avoid leaving the collar on when not training or supervising, as it can pose a safety risk if caught on objects.
9. Harnesses
9.1 Basic Design and Function
Harnesses are collar alternatives that distribute pressure more evenly across the dog’s body. They consist of straps that wrap around the chest and torso, with leash attachments located on the back or front of the dog.
9.2 Best Suited for
Harnesses are best suited for dogs with respiratory issues, are prone to pulling, or need additional support during walks. They are suitable for all breeds and sizes, with various harness types available to cater to specific needs and training goals.
9.3 Pros and Cons
One of the main advantages of harnesses is their ability to reduce strain on the neck and throat, particularly for dogs prone to respiratory issues. They provide excellent control over pulling behavior and are useful for dogs that require additional support. However, some dogs may learn to pull more with certain harness types, and improper fitting can lead to discomfort or rubbing.
9.4 Proper Usage Tips
Consider the design, adjustability, and attachment points to choose the right harness for your dog. Front-clip harnesses are effective for managing pulling behavior, while back-clip harnesses provide a more comfortable fit. Ensure that the harness is properly fitted and does not restrict your dog’s movement. Regularly inspect it for signs of wear and adjust as needed.
11. Professional Guidance and Training Program
11.1 Consulting a Veterinarian or Professional Dog Trainer
While this comprehensive article provides an overview of the different types of collars and their usage, it is essential to seek professional guidance when choosing and utilizing a collar for your dog. A veterinarian or professional dog trainer can assess your dog’s specific needs, behavior, and training goals, and offer personalized recommendations.
11.2 Customized Training Programs
A professional dog trainer can provide customized training programs that incorporate the appropriate collar and training techniques based on your dog’s individual needs. They can guide you through the training process, offering step-by-step instructions and addressing any challenges or concerns.
11.3 Long-Term Training Strategies
Long-term training strategies are essential for achieving lasting results. A professional trainer can guide continued training, reinforcement techniques, and behavior modification to ensure your dog’s training progresses successfully. They can also assist in transitioning to other collar types as your dog’s training improves or their needs change.
Choosing the suitable collar for your dog is crucial for their safety, comfort, and practical training. By considering factors such as breed, temperament, training goals, and physical limitations, you can make an informed decision that suits your dog’s needs. Remember to seek the guidance of professionals, follow proper usage tips, and prioritize positive reinforcement techniques for successful and enjoyable training experiences with your furry companion.